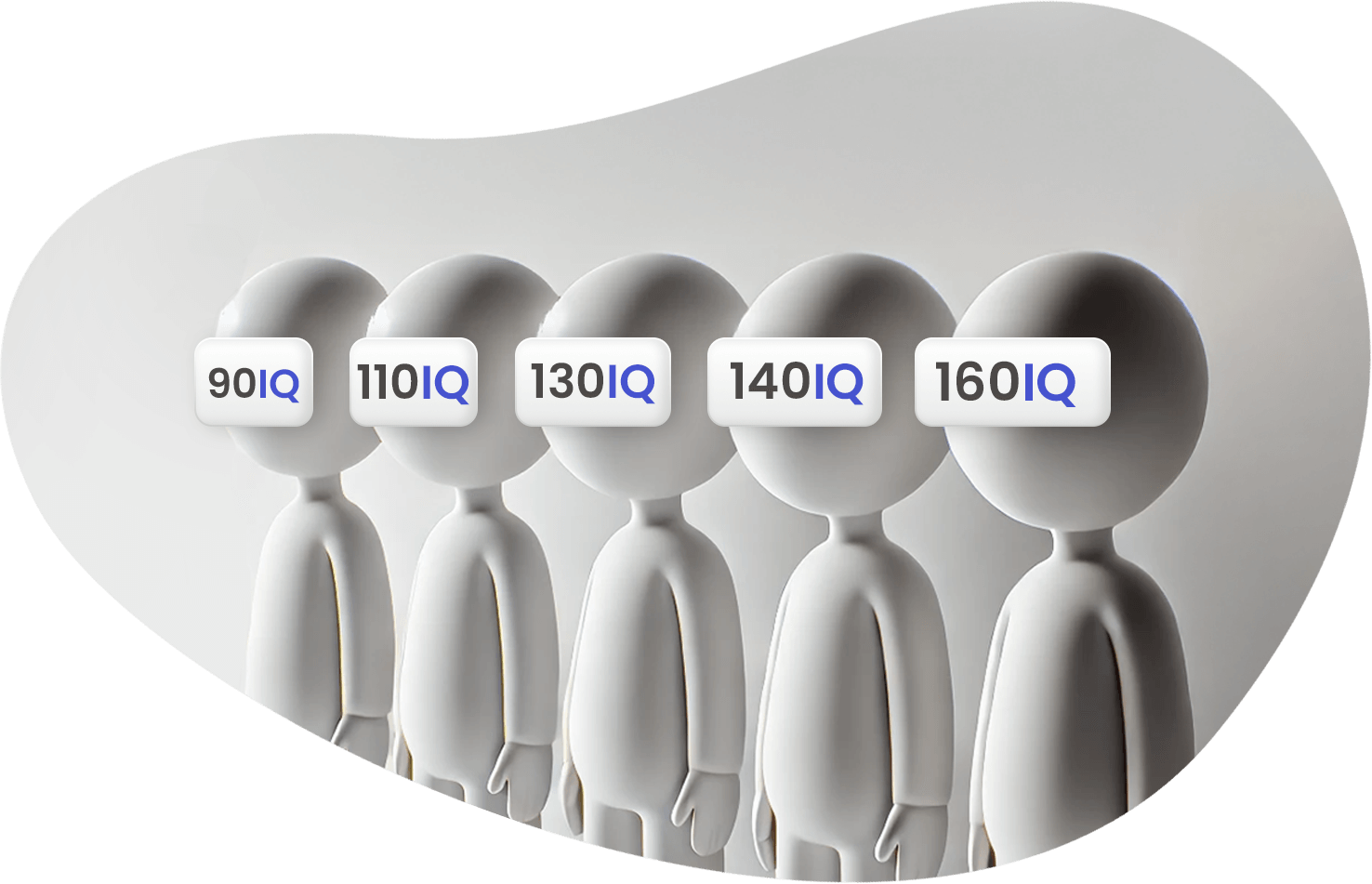
IQ Levels
IQ, or Intelligence Quotient, is a score from a test that measures a person’s thinking skills and problem-solving abilities.
An IQ test doesn’t define a person’s worth or potential, but it gives an idea of how one might perform compared to others of the same age.
This page explains IQ levels, how scores are classified, and what each level means.

What Is an IQ Score?
Introduction to Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
An IQ score is a number that represents how well someone performs on tests designed to measure different types of mental abilities, like problem-solving, logical reasoning, and memory.
It’s a way to compare a person’s cognitive abilities to the general population, with the average score being 100.
According to research conducted by Stanford University, while IQ testing measures cognitive abilities, it should not be seen as a definitive measure of a person’s potential or intelligence. Indeed, Intelligence is a multi-layered trait influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Besides, current research points to the role of developmental factors, such as prenatal health and early education, as substantial contributors.
How Are IQ Scores Measured?
IQ scores are measured with tests that check skills like logic, memory, language, and math. Traditional tests are given in controlled settings to make sure they are fair and consistent. Online intelligence tests are also popular now. They offer a quick and easy way to measure cognitive skills.
While online tests may not be as strictly controlled, good ones are designed to be reliable and accurate. Researchers work to make sure these tests measure what they are supposed to, ensuring their reliability and validity.
Controlled test settings, whether in-person or online, help reduce outside factors and give a better picture of a person's thinking abilities.
How Have IQ Tests Evolved?
Historical Background of IQ Testing
The concept of IQ testing was pioneered in the early 20th century as psychologists sought ways to quantify human intelligence. Lewis M. Terman, a professor at Stanford University, was instrumental in this effort, revising an intelligence test originally developed by Alfred Binet.
Terman’s adaptation, known as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales, became one of the most widely used tools for measuring intelligence in children and adults. In his foundational work called The Measurement of Intelligence, Terman introduced systematic methods for assessing cognitive abilities, which laid the groundwork for modern IQ testing practices and informed standardized testing protocols used today.
Types of Modern IQ Tests
Today’s intelligence tests have become more sophisticated, providing a deeper and more detailed understanding of cognitive abilities.
Two of the most recognized intelligence tests include:
Wechsler Intelligence Scale (WAIS-IV)
Considered the gold standard for adult intelligence testing, the WAIS-IV assesses a broad range of skills, including:
- Verbal Comprehension: Understanding and using language.
- Perceptual Reasoning: Solving problems using visual and spatial reasoning.
- Working Memory: Retaining and manipulating information.
- Processing Speed: Quickly and accurately completing simple tasks.
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales
Particularly effective for assessing children and young adults, the Stanford-Binet test covers essential areas like:
- Fluid Reasoning: Solving novel problems.
- Knowledge: Understanding acquired information.
- Quantitative Reasoning: Working with numbers and logic.
- Visual-Spatial Processing: Interpreting and understanding visual information.
- Working Memory: Retaining and processing information over short periods.
Intelligence tests are like windows into different parts of how our minds work. Each one is designed to measure specific aspects of brainpower, giving us pieces of the bigger puzzle of intelligence.
For example, tools like the Cognitive Assessment System or the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children focus on evaluating particular cognitive skills, such as problem-solving or memory.
These tests help identify what someone is great at and where they might need extra support. Together, these assessments create a well-rounded picture of a person’s unique mental strengths and challenges.
In short, each test brings its own flavor, contributing to a fuller understanding of how people think and learn.
What Do IQ Scores Mean?
IQ Score Ranges Explained
IQ scores are classified to interpret a person’s performance in relation to others. These classifications allow psychologists and educators to better understand where an individual falls in comparison to the general population.
Here’s a breakdown of common IQ classifications:
- 145 and above (Genius or near-genius): Represents exceptional intellectual ability. Individuals in this range often excel in complex problem-solving, abstract thinking, and may demonstrate high creativity and originality.
- 130-144 (Very high intelligence): Significantly above average; people in this range typically handle complex ideas well, excel academically or professionally, and can think critically and analytically. This is usually what we mean by “high IQ”.
- 120-129 (High intelligence): Above average, often associated with strong academic performance and quick comprehension of new concepts. Individuals in this range may excel in specialized fields and learn new skills.
- 110-119 (Above average intelligence): Slightly above average. People in this range usually have good reasoning abilities, analytical skills, and a strong grasp of moderately complex material.
- 90-109 (Average intelligence): The majority of people fall within this range. This corresponds to typical cognitive abilities. Individuals here manage everyday tasks, problem-solving, and learning without difficulty. The golden mean is 100.
- 80-89 (Below average intelligence): Somewhat below average. People in this range may encounter challenges with more complex tasks but are generally capable of independent functioning in daily life.
- 70-79 (Borderline intellectual functioning): Individuals may require additional support with certain learning or problem-solving tasks. They often manage well with guidance for routine tasks but may face challenges in academic or work settings.
- Below 70 (Intellectual disability): This range is often associated with intellectual disabilities, where individuals may require significant support in learning, self-care, and daily functioning, especially for tasks involving reasoning and complex problem-solving.
Understanding IQ Distribution
IQ scores follow a "normal distribution," meaning they fall into a predictable pattern. This pattern is called a bell curve because it resembles the shape of a bell when graphed. Most people score around the middle of the bell curve, while very high or low scores are less common. Let's break down this concept further.
Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is a measure that shows how spread out scores are in a group. In IQ testing, one standard deviation is typically 15 points. For example:
- A score of 115 is one standard deviation above the average of 100.
- A score of 85 is one standard deviation below the average.
This concept helps researchers understand the variation in IQ scores and how individuals compare to the average test score.
Try our accurate online IQ Test. Get your IQ score immediately.
Start IQ Test
Z-Score
A z-score measures how far a score is from the average in terms of standard deviations. For example:
- A z-score of +2 corresponds to an IQ score of approximately 130 (100 + 2 × 15).
- A z-score of -2 corresponds to an IQ score of approximately 70 (100 - 2 × 15).
So, the example is correct assuming an IQ test with a standard deviation of 15, which is common for tests like the WAIS-IV and Stanford-Binet. However, it's worth noting that different tests might have different standard deviations (though 15 is typical).
Bell Curve
The bell curve, or normal distribution, illustrates that most people score near the average IQ, while only a few achieve very high or very low scores. This pattern explains why average scores are the most common and extreme scores are rare.
IQ scores follow a bell curve distribution, with the majority of the population falling within the average range:
- 2% of the population score above 130.
- 14% score between 115 and 129.
- 68% score between 85 and 115 (the average IQ range).
- 14% score between 70 and 84.
- 2% score below 70.
This distribution illustrates that most people have average test scores, with fewer individuals achieving significantly higher or lower IQ scores.
Why Do IQ Levels Vary Across the World?
High Average IQs in Certain Regions
Research from various sources indicates that certain regions show higher average IQ scores. East Asian countries, such as Singapore, South Korea, and Japan, often report the highest average IQ in some datasets. Factors contributing to these higher IQ scores include:
- Educational Systems: Rigorous academic curricula encourage cognitive development.
- Cultural Values: Societal emphasis on education and achievement.
- Environmental Factors: Access to quality nutrition and healthcare.
Such factors demonstrate how environmental and cultural elements can impact cognitive performance across different regions.
Regions with Lower Average IQ Scores
Conversely, some regions have lower average IQ scores. Studies have shown that various factors can influence these lower scores:
- Limited Access to Education: Inadequate educational infrastructure hinders learning opportunities.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor nutrition during critical developmental periods affects brain development.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins or diseases can impair cognitive function.
- Socioeconomic Conditions: Poverty and instability limit access to resources. This can lower your IQ.
- Chronic stress and trauma. Persistent stress from factors such as unsafe living conditions, family instability, or community violence can negatively affect brain development and cognitive functioning, particularly in children.
It's important to approach global IQ variations with sensitivity, recognizing that socioeconomic and environmental factors play significant roles.
What Types of IQ Tests Exist?
IQ tests come in various forms, each designed to measure intelligence in specific ways and for different purposes. From professionally administered assessments to quick online quizzes, understanding the types of IQ tests can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Here's a breakdown:
Standard IQ Tests
Standard IQ tests are administered under controlled conditions by qualified professionals to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Clinical Assessments
- Administered by Professionals: Psychologists or trained specialists conduct the tests.
- Controlled Environments: Testing conditions are standardized to minimize external influences.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Assess multiple cognitive domains to provide a detailed profile.
Educational Testing
- Used in Schools: Helps identify students who may need additional support or advanced programs.
- Cognitive Aptitude Tests: Measure abilities related to learning and problem-solving.
- Educational Planning: Results assist in developing tailored educational strategies.
Online IQ Tests
Online IQ tests have become popular due to their convenience and accessibility. However, they have limitations:
- Less Accurate: Generally less reliable than standardized IQ tests administered by professionals. However, adaptive online IQ tests, which adjust the difficulty of questions based on your answers, are more accurate than fixed-format online tests.
- For Entertainment: Often intended for fun rather than serious assessment.
- Uncontrolled Conditions: Cannot account for testing environment variables.
- Limited Validation: Lack rigorous scientific validation and standardization.
While online IQ tests can be useful for practice or curiosity, they should not be considered definitive measures of intelligence.
Try our 100% adaptive online IQ Test. Get your IQ score within minutes.
Launch IQ Test
Are There Special Considerations for IQ Testing?
IQ Testing in Children
Assessing the intelligence of children is a nuanced process that goes beyond measuring academic achievement. It requires recognizing and understanding the unique traits and characteristics that set gifted children apart. According to the Davidson Institute's research, giftedness is not solely reflected in high grades or traditional success but also in attributes like curiosity, creative problem-solving, and a deep need for intellectual stimulation. These distinctions make early identification and tailored support essential.
Key considerations in testing include:
- Early Identification: Testing can identify exceptional abilities, allowing for appropriate educational support.
- Developmental Variability: Children's cognitive abilities can change rapidly as they grow.
- Environmental Factors: Home environment and educational opportunities significantly impact development.
- Regular Reassessment: Periodic testing may be necessary to monitor progress.
It's essential to interpret children's IQ scores with caution, considering the broader context of their development.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence
Traditional IQ tests focus on cognitive abilities but may overlook emotional intelligence (EQ), which is also very important.
EQ involves:
- Social Understanding: Navigating social situations effectively.
- Emotional Awareness: Recognizing and managing one's own emotions and those of others.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building and maintaining relationships.
- Adaptive Abilities: Adjusting to new situations and challenges.
Emotional intelligence contributes significantly to personal and professional success, complementing cognitive intelligence.
What Factors Influence IQ Scores?
Environmental Factors Affecting IQ
IQ scores are shaped by a variety of environmental influences, which play a crucial role in cognitive development.
- Educational Opportunities: Access to quality education fosters intellectual growth and critical thinking.
- Socioeconomic Status: Economic stability offers resources and opportunities that support learning.
- Nutrition and Health: Proper nutrition and healthcare are essential for healthy brain development.
- Early Childhood Experiences: Stimulating and enriching environments during early childhood lay the foundation for lifelong learning.
Targeted interventions in these areas can significantly enhance cognitive functioning and positively impact IQ scores.
Genetic Factors in Intelligence
Genetics also play a key role in determining intelligence. Studies from UC Berkeley suggest that genetics also play a significant role:
- Hereditary Influences: Intelligence can be inherited from one's parents.
- Gene-Environment Interactions: Genetics and environment work together to shape cognitive abilities.
- Complex Inheritance Patterns: Multiple genes contribute to general intelligence.
- Genetic Predisposition to Learning Styles: Genetic factors may influence not only general intelligence but also specific cognitive styles and learning preferences.
How Does Your IQ Level Impact Education and Career?
IQ and Educational Success
There is a strong relationship between IQ and academic performance, as shown in research from Nature. Higher IQ scores are often linked to better grades and learning outcomes, making IQ a helpful tool in educational planning and identifying areas where students might need additional support.
In addition, social skills like teamwork and communication can enhance collaborative learning, allowing students to benefit from group discussions and shared problem-solving. Perseverance, often referred to as "grit," helps students push through challenges and setbacks, ensuring they stay on track even when the material is difficult.
Interestingly, even a person’s mindset can influence how their IQ impacts education and career success. A growth mindset, or the belief that intelligence and abilities can improve with effort, can enhance learning outcomes regardless of IQ level. Students with this mindset are more likely to embrace challenges, persist through difficulties, and view failure as an opportunity to grow.
Interestingly, qualities like curiosity, adaptability, and creative problem-solving are often considered signs of high IQ. These traits not only reflect cognitive ability but also fuel success in academic settings. For example, curiosity drives students to explore topics beyond the classroom, while adaptability allows them to navigate unexpected challenges effectively. Similarly, creative problem-solving enables students to find innovative solutions, which is particularly valuable in subjects requiring critical thinking.
Ultimately, while IQ can provide a helpful starting point, it’s only part of the equation. Success in school is shaped by a combination of cognitive ability, personal qualities, and external factors like teaching quality and support systems.
IQ in the Workplace
In the workplace, IQ can influence various aspects of job performance:
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Essential for roles requiring critical thinking and high level decision making.
- Leadership Potential: Intelligence contributes to effective decision-making and strategy.
- Innovation Capabilities: Cognitive abilities support creativity and the development of new ideas.
- Adaptability to New Technologies: Higher cognitive abilities can assist in quickly learning and adapting to new technologies or complex systems, which is increasingly important in today’s rapidly evolving workplaces.
While higher IQ scores can be advantageous, they are not the sole determinant of professional achievement and workplace effectiveness. Other factors, such as emotional intelligence, experience, and strong interpersonal skills, also play critical roles.
Common Misconceptions About IQ
Is IQ Fixed?
A common misconception is that IQ is unchangeable. Research indicates that IQ can change over time:
- Childhood Development: Significant brain development occurs during childhood, affecting cognitive abilities.
- Environmental Influences: Education, nutrition, and life experiences can lead to higher IQ scores.
- Educational Interventions: Programs targeting specific skills can improve cognitive function.
- Lifelong Learning: Continued learning and mental challenges can enhance intelligence.
- Neuroplasticity: The brain’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections means that cognitive abilities, including IQ, can adapt and improve in response to learning and new experiences throughout life.
Does a High IQ Equal Success?
Another misconception is that a high IQ guarantees success. Studies show that success depends additionally on multiple factors:
- Emotional Intelligence: EQ is equally as important as IQ for success. Managing emotions and relationships is crucial in personal and professional settings.
- Persistence and Dedication: Hard work and perseverance often outweigh innate ability.
- Adaptability and Resilience: The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and bounce back from setbacks is often more predictive of long-term success than IQ alone.
- Social Skills: Effective communication and teamwork are essential.
- Practical Intelligence: Common sense and problem-solving in real-world situations are valuable.
Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions About IQ Levels
What is the Average IQ?
The average IQ score is standardized at 100, which represents the middle point of the IQ scale. This score is considered the "benchmark" because it reflects the average cognitive ability of the general population. This means most people score near 100 on IQ tests, and this average remains consistent worldwide.
This benchmark allows test designers to develop questions that are fair and relevant for various age groups and cultural backgrounds, enabling meaningful comparison of scores across individuals of different ages and backgrounds.
The standardization around 100 ensures that IQ tests remain a reliable tool for measuring cognitive ability relative to the population.
What is a Normal IQ?
An IQ score within the range of 85 to 115 is typically considered "average" or "normal". This range includes about 68% of people, meaning most people fall within this band. If someone scores in this range, they are considered to have typical cognitive abilities, which means they perform similarly to most people on tasks that require thinking, problem-solving, and memory.
People with scores in the normal range are generally able to handle everyday challenges and understand most ideas without external assistance.
What is a Good IQ Score?
A score above 110 is generally considered above average, so scores in this range are often viewed as "good." People in this category may find learning new things easier and tend to do well on tasks that involve reasoning or complex thinking. However, any score between 90 and 109 is considered perfectly normal and sufficient for most life situations. Research from Stanford University shows that while higher IQ scores can help in certain areas, success in life isn’t determined solely by IQ; factors like social skills, dedication, and creativity are equally important.
What is a High IQ Score?
A high IQ score is generally considered to be above 120. People with scores in this range often have strong problem-solving abilities and may excel in academic or intellectual areas. They may also find it easier to think abstractly or connect different ideas quickly. High IQ can be an advantage in fields that require complex thinking, like science or engineering. However, while a high IQ can indicate strong intellectual abilities, it doesn’t guarantee success, as motivation, personality, and perseverance play a major role in achieving goals.
What is a Genius-Level IQ?
A genius-level IQ is typically considered to be 130 or above, with scores of 145 or higher often regarded as exceptionally rare. People with these scores are very rare and often display exceptional abilities in problem-solving, creativity, and original thinking. This category includes well-known geniuses and highly talented individuals who make unique contributions to fields like science, technology, and the arts. However, having a genius-level IQ doesn’t necessarily mean a person will become famous, rich or highly successful. It is one aspect of intelligence that, when combined with other factors like motivation, perseverance, and opportunity, can contribute to extraordinary accomplishments.
Can IQ Scores Change Over Time?
Yes, IQ scores can change, especially during childhood and adolescence. Factors such as education, life experiences, and mental challenges can all influence IQ. For example, engaging in activities that stimulate the brain, like reading, solving puzzles, or learning new skills, may positively impact IQ. Environmental influences, such as nutrition and access to education, can also play a role. While adults may see smaller changes, studies suggest that continued learning, mental challenges, and a stimulating environment can help enhance cognitive abilities over time.
How Accurate are Online IQ Tests?
Online IQ tests can be entertaining and provide a rough estimate of your intelligence, but they’re generally less reliable than professional assessments. Most of these tests lack the controlled conditions, rigor, and cultural neutrality of standardized IQ tests administered by professionals. They tend to focus on a narrow range of question types, ignoring the complexity and variety of cognitive abilities measured in professional assessments.
However, not all online IQ tests are created equal. Adaptive online IQ tests like CheckIQ, which adjust the difficulty of questions based on your previous answers, are significantly more accurate than the fixed-format tests you can find everywhere. These adaptive tests mimic the approach of professional assessments by tailoring the test to your ability level, making them better at estimating your IQ. Even so, while adaptive IQ tests are a step up, they still can’t match the precision of a professionally administered test.
For a truly valid IQ assessment, it’s best to consult with a trained professional who can provide a standardized and comprehensive evaluation.
Testing and Methodology
What’s the Difference Between Standard IQ Tests and Cognitive Aptitude Tests?
Standard IQ tests measure general intelligence, which includes broad cognitive abilities like reasoning, problem-solving, and memory. Cognitive aptitude tests, on the other hand, target specific skills, such as spatial reasoning or verbal abilities. For example, a cognitive aptitude test might focus only on a person’s ability to solve math problems or understand language. While both tests assess mental abilities, IQ tests give a more comprehensive view of a person’s overall intelligence, whereas cognitive aptitude tests offer a more targeted assessment of specific intellectual domains.
Are IQ Tests Biased?
Modern IQ tests aim to be as fair as possible by designing questions that minimize bias. However, some factors, like a person’s cultural, social, or economic background, can still influence test performance. For instance, someone who grew up with limited access to books or schooling may not perform as well on a test that includes vocabulary or general knowledge questions. While researchers and test designers make significant efforts to reduce these biases, it is challenging to eliminate all cultural influences. Therefore, IQ scores should be seen as just one aspect of a person’s cognitive abilities, not a definitive measure of their overall potential.
How is IQ Testing Different for Children?
IQ testing for children, like the Stanford-Binet test, is specifically designed to take developmental stages into account. Children’s IQ tests focus on skills appropriate for their age, such as simple problem-solving, memory, and understanding of basic concepts. Moreover, children's IQ scores can change over time as they grow, which is why retesting may be recommended, particularly for younger children. IQ testing can help identify giftedness or learning needs early on, allowing parents and educators to provide appropriate support. However, it’s important to keep in mind that a child’s IQ score is just one aspect of their development and should be considered alongside other abilities and interests.