SAT to IQ Calculator
The Scholastic Assessment Test (SAT) has long been a cornerstone of college admissions in the United States. Beyond its role in evaluating college readiness, many have debated whether the SAT is a measure of intelligence. This article explores the relationship between SAT scores and IQ scores, examines the validity of converting SAT scores to estimated IQ, and discusses various perspectives backed by research.
What Is the SAT?
The Scholastic Assessment Test (SAT) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Administered by the College Board, the SAT assesses high school students' readiness for college by evaluating critical reading, writing, and mathematical reasoning abilities developed throughout their secondary education.
First introduced in 1926 as the Scholastic Aptitude Test, the SAT was designed to democratize access to college by providing a standardized measure for all applicants, regardless of their high school background. This allowed colleges to compare students from different schools on an equal footing, helping to level the playing field in the admissions process.
While the SAT was originally adapted from the Army IQ test and shares similarities with intelligence tests, it has importantly evolved over the decades to measure developed and learned skills rather than innate ability. Critics, however, argue that despite these changes, the SAT’s origins and its limited ability to predict long-term success in college and beyond raise concerns about its fairness and relevance.
Over time, the test has evolved to reflect changes in education and testing philosophy. High school students now encounter an SAT that focuses more on the skills and knowledge essential for college and career success. In 2016, the College Board implemented a significant redesign of the SAT.
Key changes included:
- Optional Essay: The essay section became optional, allowing students to decide whether to showcase their writing skills.
- Evidence-Based Reading and Writing: The test shifted focus to evidence-based reading and writing, emphasizing the interpretation, synthesis, and use of evidence found in a wide range of sources.
- Mathematics: The math section was updated to reflect real-world problem-solving skills, concentrating on areas that matter most for college and career readiness, such as algebra, data analysis, and advanced math topics.
- No Penalty for Wrong Answers: The redesigned SAT eliminated the penalty for incorrect answers, encouraging students to attempt all questions without fear of losing points for guesses, thus better reflecting their true knowledge and abilities.
These changes aimed to make the SAT more relevant to what high school students learn in the classroom and better aligned with college expectations.
A reliable 100% adaptive online IQ Test. Get your IQ score immediately.
Start My IQ Test
What Does the SAT Measure?
The SAT tests your reading, writing, and math skills. It checks how well you can understand and analyze information, solve problems, and use math concepts. The test focuses on what you've learned in school and life over time, and not in just pure or gifted talent.
Some people think the SAT measures intelligence. However, it is really about the skills and knowledge you've built up and its main goal is to see if you're ready and well-prepared for college-level work.
Does IQ Correlate with SAT Scores?
The SAT is primarily known as a college admission test. But according to research, SAT scores correlated pretty well with intelligence quotient (IQ). A study by Frey and Detterman (2004) revealed a strong connection between SAT scores and IQ, with a correlation as high as 0.82! This means that people who score well on IQ tests often do well on the SAT.
Psychologists like David Hambrick and Christopher Chabris support that idea. Hambrick explains that the SAT's alignment with standardized IQ tests is a result of the SAT’s focus on reasoning, problem-solving, and comprehension skills. He notes that, like IQ tests, SAT scores remain relatively stable over time and are not easily improved through test preparation alone, further reinforcing the connection between the two.
Does a Low SAT Score Mean a Low IQ?
Not necessarily! A low SAT score doesn’t automatically mean a low IQ, as there is no direct cause-effect relationship between the two. Since the SAT and IQ tests measure different things, many factors can influence a test-taker's performance on the SAT.
The SAT evaluates skills like critical reading, writing, and math that are developed through education and practice. On the other hand, an IQ test focuses on measuring general cognitive abilities and problem-solving potential. While there is some correlation between SAT scores and IQ, they are not the same.
A low SAT score might reflect other challenges, such as test anxiety, unfamiliarity with the test format, or lack of preparation. These factors don’t indicate someone’s innate intelligence or cognitive potential. Test-takers may excel in areas not measured by the SAT or demonstrate their intelligence in ways beyond standardized testing.
In short, a low SAT score doesn't define your cognitive abilities or overall potential. It is just one aspect of a much broader picture.
Is the SAT a Measure of Intelligence?
Since IQ correlates well with SAT test scores, we would expect it to also correlate well with intelligence.
However, the SAT is not purely an intelligence test. Unlike standardized IQ tests such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), the Stanford-Binet test or the Raven’s Progressive Matrices, which focus on problem-solving and reasoning, the SAT also evaluates skills gained through education and life experiences. For example, it tests vocabulary, mathematical concepts, and reading comprehension, all of which can be influenced by years of learning.
As Frey and Detterman explained, the SAT is a mix of "general cognitive ability and academic achievement." It doesn’t measure innate intelligence alone but combines elements of intelligence with effort, education, and preparation. This means the SAT serves as both a measure of cognitive function and a reflection of a student’s academic progress and effort. Thus, while it really provides some insight into intellectual ability, it is not a comprehensive measure of intelligence.
Does the SAT Predict College Success ?
Yes, the SAT is a good predictor of college success, but it goes beyond that. Research published in Psychological Science shows that SAT scores are just as reliable as high school grades in predicting a student’s GPA during their first year of college.
But the SAT’s usefulness doesn’t end with college. Studies have found that SAT scores also relate to long-term achievements, like career success and income. This means the skills the SAT tests, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and reasoning, are valuable not only in school but also in life.
These findings suggest that the SAT measures more than academic knowledge. It evaluates cognitive abilities that are essential for success in many areas. As a result, the SAT is not only a measure of academic potential but also an indicator of broader life potential.
How Can You Convert SAT Scores to Estimated IQ?
Converting SAT scores to estimated IQ test scores is a complex process due to the differences in how the two tests are designed and standardized. However, some psychologists and researchers have attempted to create conversion tables based on statistical correlations between the two tests. It's important to note that these conversions are approximate and should be taken with caution. The SAT and IQ tests measure overlapping but not identical constructs, and individual results may vary.
In the case of our SAT to IQ converter, we rely on percentile matching, which involves comparing your ranking among SAT test-takers to the equivalent ranking in an IQ distribution. To ensure accuracy, we use official SAT score distribution charts provided by the College Board to determine the percentile rank of your SAT score.
For instance, if your SAT score places you in the 90th percentile, meaning you scored higher than 90% of SAT test-takers, we match that percentile to the corresponding percentile in an IQ distribution, assuming a standard deviation (SD) of 15, which is standard for IQ scoring.
This method provides a rough estimate of IQ based on SAT performance. However, it’s important to note that these conversions are approximate. Factors like test preparation, educational background, and test-taking strategies can influence test takers’ SAT scores differently from IQ tests. While our converter offers an insightful estimate, it is not a substitute for a professionally administered IQ test.
SAT Score Percentiles and Corresponding IQ Score
Here's a simplified table matching SAT scores to estimated IQ scores based on percentile ranks:
|
SAT Score |
SAT Percentile |
Estimated IQ |
|
1600 |
99.9th |
145 |
|
1500 |
98th |
135 |
|
1400 |
94th |
125 |
|
1300 |
87th |
117 |
|
1200 |
74th |
110 |
|
1100 |
59th |
105 |
|
1000 |
41st |
97 |
|
900 |
26th |
90 |
|
800 |
13th |
85 |
Note: These are approximate values intended for illustrative purposes.
How to use our SAT to IQ Conversion Tool
In our SAT to IQ converter, we rely on percentile ranks to provide an estimated IQ score corresponding to a given SAT score (and vice-versa):
SAT to IQ conversion:
- Enter your SAT score
- Let the converter calculate your equivalent IQ
IQ to SAT conversion:
This tool allows you to:
- Enter your IQ score (*)
- Let the converter calculate your equivalent SAT score
(*) Use an IQ score based on a 15-point standard deviation.
Celebrities with High SAT Scores
Several celebrities have shared their SAT scores publicly. According to Best College some notable scores include:
- Mark Zuckerberg: 1600 (Perfect score)
- Ben Affleck: Near 1600 (Perfect score)
- Will Smith: Near 1600 (Perfect score)
- Kesha: 1500
- Natalie Portman: Over 1400
- Kobe Bryant: 1080
- Courtney Cox: 1150
These scores demonstrate that high SAT performance is not exclusive to academic achievers but can also be found among successful individuals in a wide range of fields.
Do High-IQ Societies Accept Sat Scores?
Many prestigious high IQ societies accept SAT scores as part of their membership requirements, but only under certain conditions. High IQ societies aren’t just about bragging rights. Thus, they allow you to meet like-minded people, explore big ideas, and challenge yourself. If your SAT scores fit the bill, why not give it a shot?
Here’s a simple guide to help you understand:
1. International High IQ Society (IHIQS)
If your SAT score places you in the top 5% (95th percentile), you may qualify for membership. This society is a welcoming place for those seeking to join a community of smart individuals without intense pressure.
Here you can find more information about the International High IQ Society (IHIQS).
2. Mensa International
Mensa accepts SAT scores from 1974 to 1994 if you scored 1250 or higher. Unfortunately, newer SAT scores are not accepted for membership.
Here is additional information about Mensa International.
3. Intertel
Intertel sets a higher bar, requiring at least 1300 on SATs taken between 1974 and 1994. This society caters to those in the top 1% of intellectual ability.
More information about Intertel can be found here.
4. Triple Nine Society
For SATs taken before 1995, you’ll need a score of 1450 to qualify. If you took the test between April 1995 and February 2005, the requirement jumps to 1520. This society is for the top 0.1% – only the most elite thinkers qualify.
Additional information about the Triple Nine Society can be found here.
5. International Society for Philosophical Enquiry (ISPE)
ISPE accepts SAT scores across various timeframes:
- Before 1995: A score of at least 1450.
- After 1995 (2400 scale): A score of at least 2210.
- After 2005 (1600 scale): A score of at least 1520.
You can find more details about the International Society for Philosophical Enquiry (ISPE) here.
6. Epimetheus Society
For SATs taken before 1995, a score of 1550 or higher is required. Needless to say, this society is for individuals with exceptionally rare and outstanding intellects.
7. Mega Society
The Mega Society is the most exclusive of all, requiring scores from the 99.9999th percentile. SAT acceptance is determined on a case-by-case basis, making it the ultimate challenge for those seeking recognition of extraordinary intelligence.
Further information about the Mega Society can be found here.
Other Frequently-Asked Questions
What is the average SAT score?
Understanding the average SAT score provides valuable context for interpreting individual results.
As of 2021, the average SAT score for all test-takers was approximately 1050 out of a maximum 1600.
This average is split between the two main sections:
- Evidence-Based Reading and Writing (ERW): around 528
- Math: around 523
SAT scores follow a normal distribution, meaning most students score near the average, with fewer students achieving very high or very low scores. By understanding where your score falls in relation to the average, you can better assess your competitiveness for college admissions.
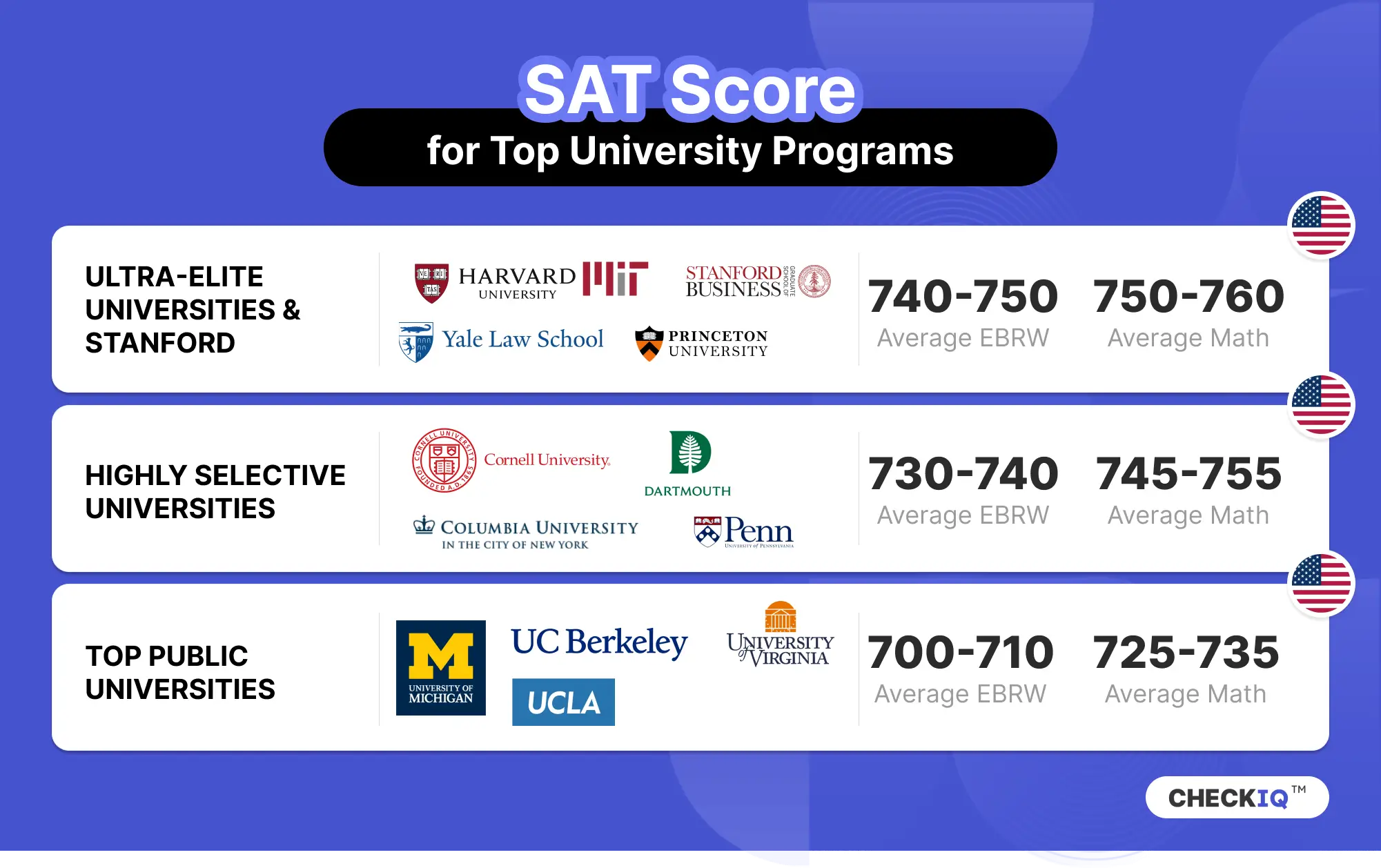
Cornell University Admission Requirements: SAT, ACT, GPA. GeeksforGeeks. Available at: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cornell-university-admission-requirements-sat-act-gpa/. Accessed January 26, 2025.
Dartmouth SAT Scores and GPA. GeeksforGeeks. Available at: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dartmouth-sat-scores-and-gpa/. Accessed January 26, 2025.
Top Universities Accepting SAT Score in 2024. GeeksforGeeks. Available at: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/top-universities-accepting-sat-score-in-2024/?ref=shm. Accessed January 26, 2025.
Freshman Admission Profile: UCLA. University of California Admissions. Available at: https://admission.universityofcalifornia.edu/campuses-majors/ucla/freshman-admission-profile.html. Accessed January 26, 2025.
University of Michigan SAT Scores and GPA. PrepScholar. Available at: https://www.prepscholar.com/sat/s/colleges/University-of-Michigan-sat-scores-GPA. Accessed January 26, 2025.
UVA SAT Scores and GPA. PrepScholar. Available at: https://www.prepscholar.com/sat/s/colleges/UVA-sat-scores-GPA. Accessed January 26, 2025.
What is the highest SAT score?
The highest possible SAT score is 1600, which represents a perfect score of 800 in both the Evidence-Based Reading and Writing section and the Math section. Achieving a perfect score is exceptionally rare.
According to the College Board’s list of SAT percentiles, only about 1% of test-takers score between 1530 and 1600 each year.
While a perfect SAT score can strengthen a student’s college application, particularly for highly competitive schools, admissions decisions also consider other important factors such as GPA, extracurricular activities, personal essays, and letters of recommendation.
What Affects SAT Performance?
Several factors influence SAT performance, including socioeconomic background and psychological elements like test anxiety. These factors can shape a test-taker's results, but they don’t fully explain the test’s ability to measure cognitive abilities.
While SES correlates with SAT scores – giving students from wealthier backgrounds better access to resources and preparation – research shows this is not the sole determinant. Even after accounting for SES, the SAT remains a strong predictor of college success, demonstrating its capacity to assess critical cognitive skills.
Psychological challenges, such as test anxiety and performance avoidance, also play a role. A study published in the journal Intelligence highlights that test anxiety, along with general intelligence and metacognitive awareness, significantly affects SAT performance.
Can test preparation significantly improve SAT scores?
The effectiveness of SAT preparation courses has been a subject of debate. While test prep can lead to some improvements, the gains are generally modest.
According to psychology professor David Z. Hambrick in his New York Times article, although SAT preparation courses can help, the average increase is usually no more than about 20 points per section.
This implies that while preparation can familiarize students with the test format and question types, it may not lead to substantial score enhancements.
Can I improve my IQ score?
IQ scores are considered relatively stable over time. While certain activities may enhance cognitive function, significant changes in IQ scores are uncommon. Focused learning and skill development can, however, improve specific abilities measured by IQ tests.
If you are committed to personal growth, you may find that consistently challenging your brain through activities like problem-solving, learning new skills, engaging in critical thinking exercises, or even reading – which is linked to an increase in intelligence –, can sharpen your cognitive abilities over time.